Soil Microbial Diversity Affects the Plant-Root Colonization by Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungi
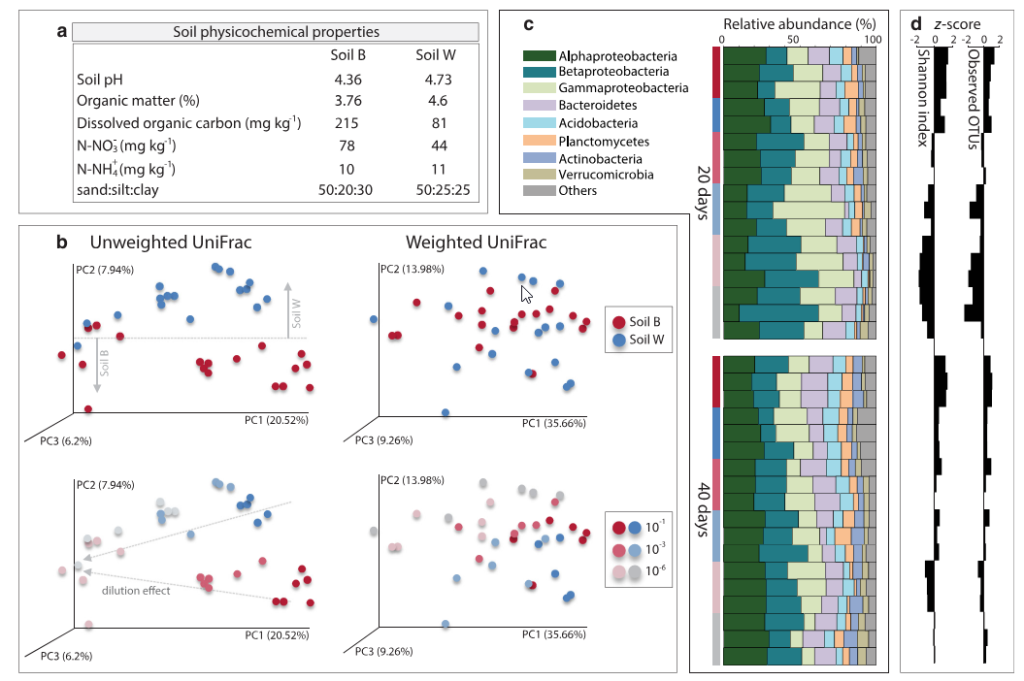
Abstract Terrestrial plants establish symbiosis with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) to exchange water and nutrients. However, the extent to which soil biodiversity influences such association remains still unclear. Here, we manipulated the soil microbial diversity using a “dilution-to-extinction” approach in a controlled pot microcosm system and quantified the root length colonization of maize plants by […]
Responses of microbial community from tropical pristine coastal soil to crude oil contamination
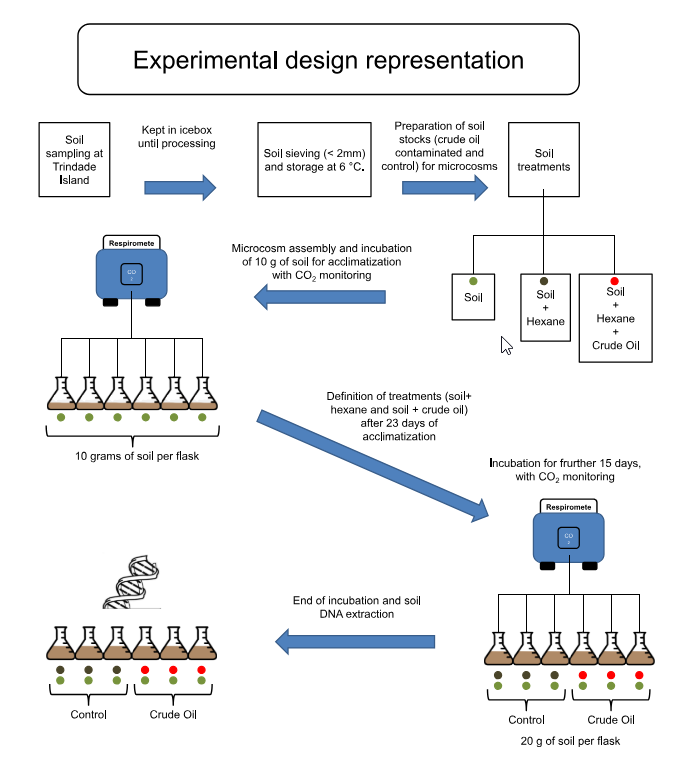
Abstract Brazilian offshore crude oil exploration has increased after the discovery of new reservoirs in the region known as pré-sal, in a depth of 7.000 m under the water surface. Oceanic islands near these areas represent sensitive environments, where changes in microbial communities due oil contamination could stand for the loss of metabolic functions, with […]
Organic practices intensify the microbiome assembly and suppress root‐knot nematodes
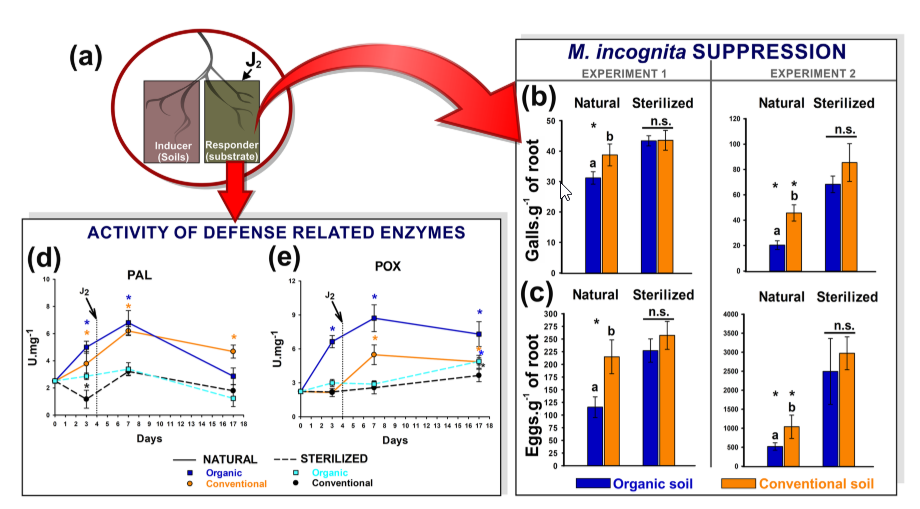
Abstract Roots can recruit beneficial microorganisms to suppress plant pathogens. However, conventional and organic practices differently shape the soil microbiome and consequently the root protection. Here, we investigated the suppressive activity of soil microbiome against the root-knot nematode (RKN) Meloidogyne incognita in horticultural areas under organic or conventional practices and the microbiome profiles in non-inoculated (RKN-absent) and […]
Moisture Is More Important than Temperature for Assembly of Both Potentially Active and Whole Prokaryotic Communities in Subtropical Grassland
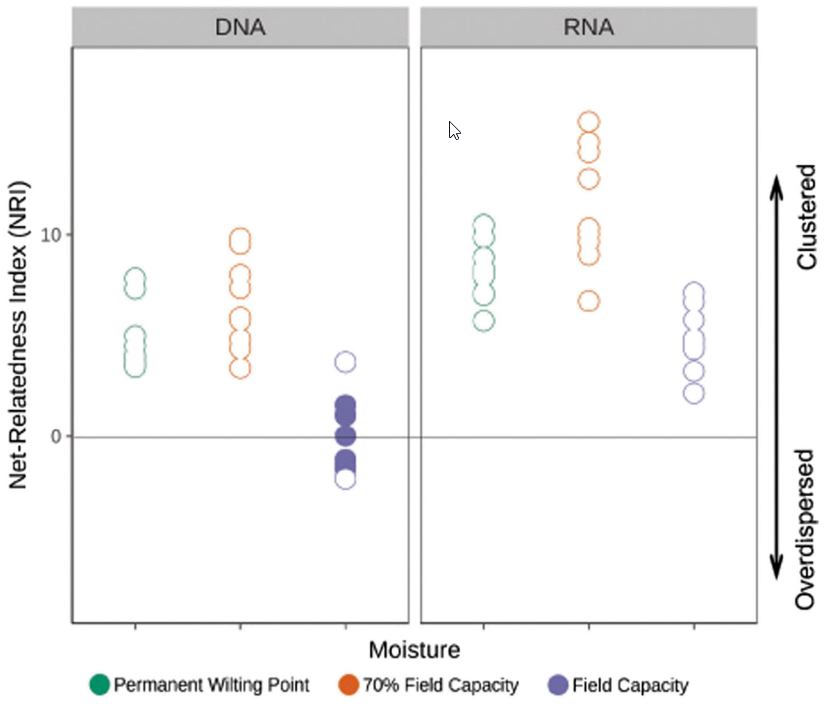

Abstract Moisture and temperature play important roles in the assembly and functioning of prokaryotic communities in soil. However, how moisture and temperature regulate the function of niche- versus neutral-based processes during the assembly of these communities has not been examined considering both the total microbial community and the sole active portion with potential for growth […]
Metagenome assembled-genomes reveal similar functional profiles of CPR/Patescibacteria phyla in soils
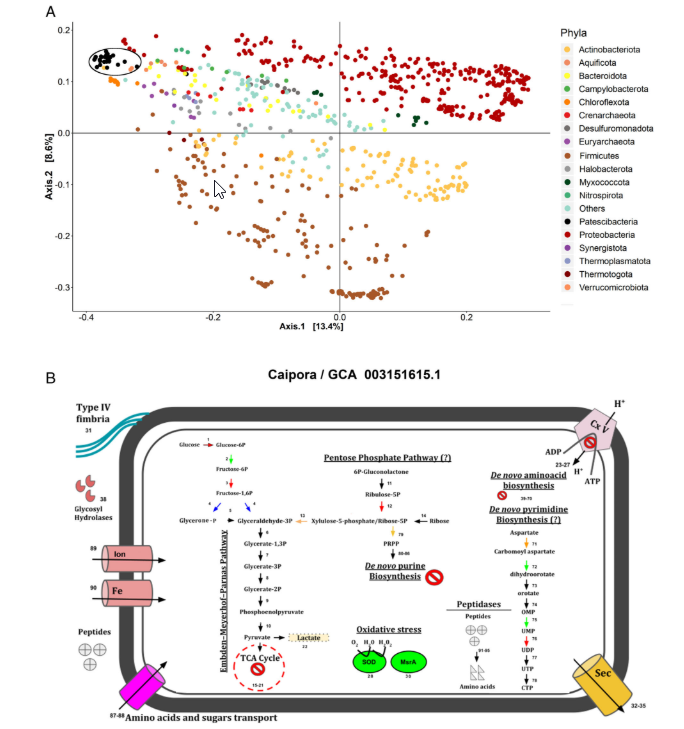
Abstract Soil microbiome is one of the most heterogeneous biological systems. State-of-the-art molecular approaches such as those based on single-amplified genomes (SAGs) and metagenome assembled-genomes (MAGs) are now improving our capacity for disentailing soil microbial-mediated processes. Here, we analysed publicly available datasets of soil microbial genomes and MAG’s reconstructed from the Amazon’s tropical soil (primary […]
Calcium Oxalate Crystals in Eucalypt Ectomycorrhizae: Morphochemical Characterization
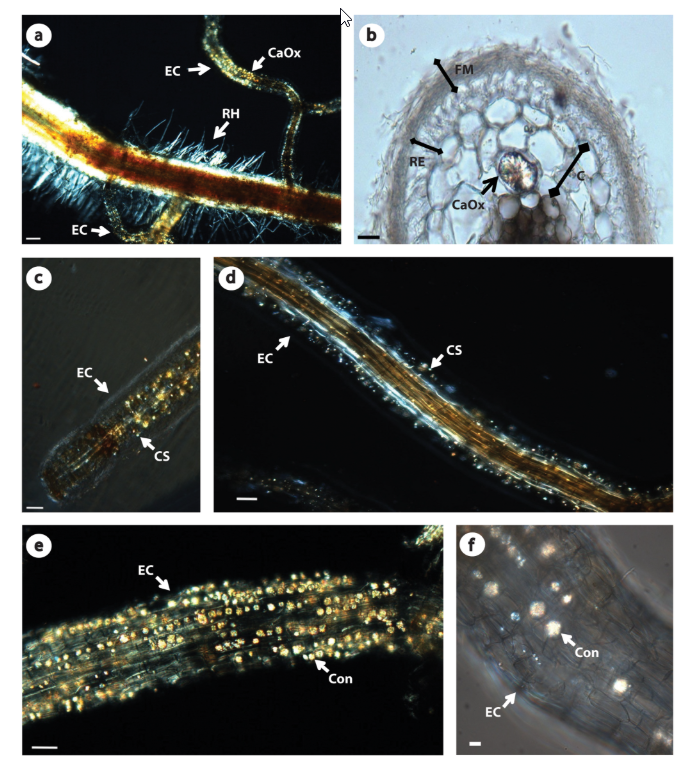
Abstract Ectomycorrhizal fungi are ubiquitous in forest ecosystems, benefitting plants principally by increasing the uptake of water and nutrients such as calcium from the soil. Previous work has demonstrated accumulation of crystallites in eucalypt ectomycorrhizas, but detailed morphological and chemical characterization of these crystals has not been performed. In this work, cross sections of acetic […]
Brazilian Microbiome Project: Revealing the Unexplored Microbial Diversity—Challenges and Prospects

Abstract The Brazilian Microbiome Project (BMP) aims to assemble a Brazilian Metagenomic Consortium/Database. At present, many metagenomic projects underway in Brazil are widely known. Our goal in this initiative is to co-ordinate and standardize these together with new projects to come. It is estimated that Brazil hosts approximately 20 % of the entire world’s macroorganism […]
Back to the Future of Soil Metagenomics

Abstract Roots can recruit beneficial microorganisms to suppress plant pathogens. However, conventional and organic practices differently shape the soil microbiome and consequently the root protection. Here, we investigated the suppressive activity of soil microbiome against the root-knot nematode (RKN) Meloidogyne incognita in horticultural areas under organic or conventional practices and the microbiome profiles in non-inoculated (RKN-absent) and […]
Fungal diversity and occurrence of mycotoxin producing fungi in tropical vineyards
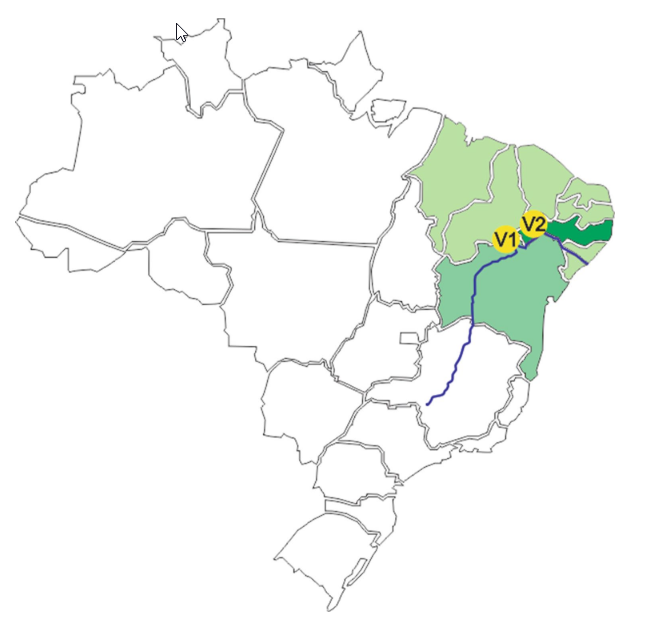
Abstract Grapevine cultivars are distributed worldwide, nevertheless the fermentation of its grape berries renders distinct wine products that are highly associated to the local fungal community. Despite the symbiotic association between wine and the fungal metabolism, impacting both the terroir and mycotoxin production, few studies have explored the vineyard ecosystem fungal community using both molecular marker sequencing […]
Simulation of coffee beans contamination by Aspergillus species under different environmental conditions and the biocontrol effect by Saccharomyces cerevisiae
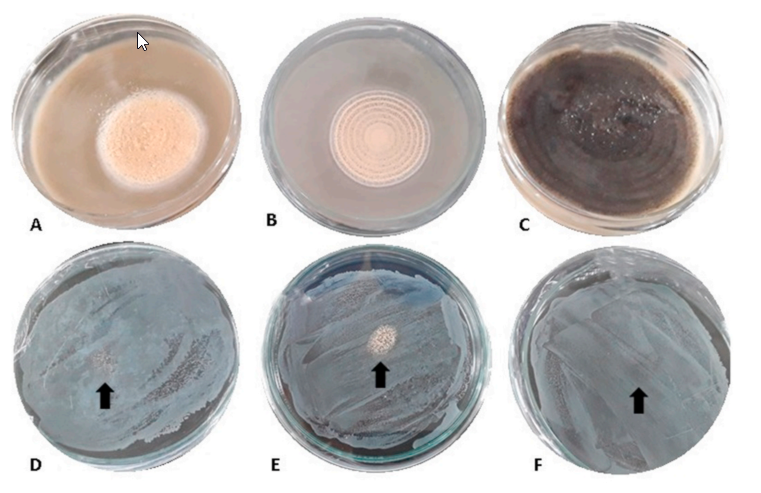
Abstract Temperature and water activity (aw) are both responsible for the growth and production of ochratoxin A (OTA) by Aspergillus species in coffee. To prove this, we tested the effect of environmental factors combined with green coffee composition on the risk of OTA production as well as the efficiency of using Saccharomyces cerevisiae to control the growth of Aspergillus ochraceus, A. […]

