Microbial diversity of Syrah grapes cultivated for winter wine production in Minas Gerais, Brazil
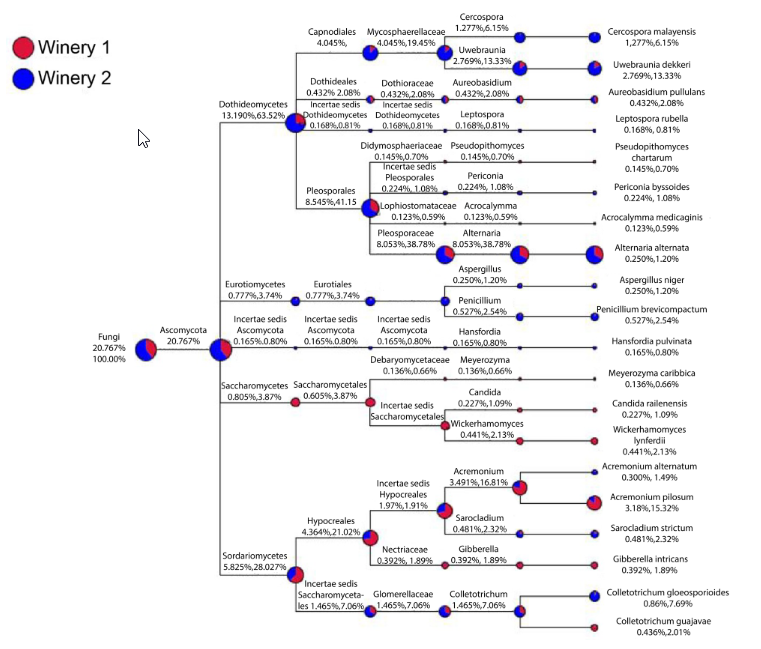
ABSTRACT Microorganisms play a key role in determining the terroir of any region where vineyards are cultivated, influencing the characteristics of the wine produced in that region. This study aimed to determine the mycobiota terroir of Syrah grapes from subtropical vineyards of southern Minas Gerais, Brazil, using independent cultivation methods. Total DNA was extracted from […]
Volatile compounds for biotechnological applications producedduringcompetitive interactions between yeasts and fungi
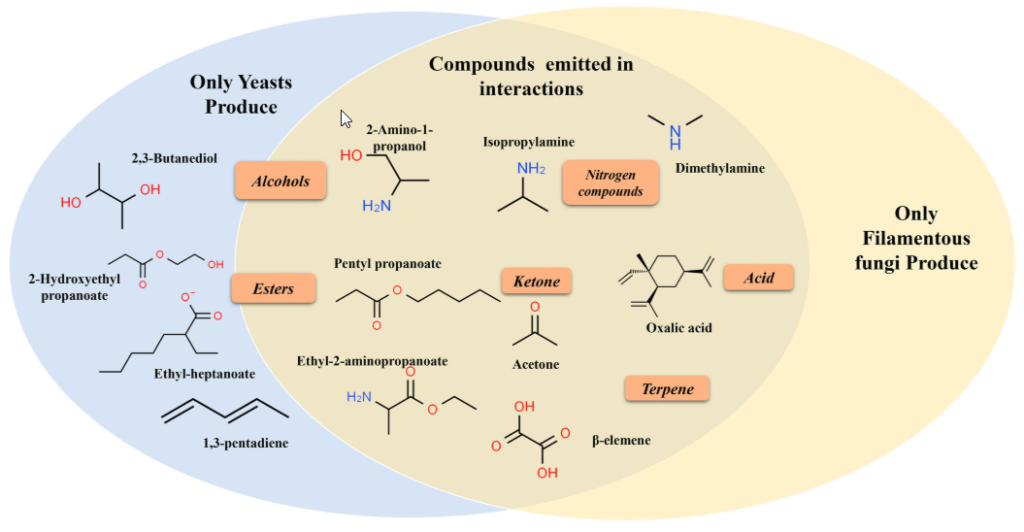
Abstract Fungi, yeasts and bacteria produce volatile compounds during their metabolism. In this study, the volatile compounds produced by yeast strains (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Rhodotorula mucilaginosa) and fungal strains (Aspergillus carbonarius and Aspergillus ochraceus) during competitive interactions were investigated by solid-phase microextraction coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Fifty-six volatile compounds were identified representing alcohols, aldehydes, esters, ketones, aromatic compounds, […]
The antibacterial, antioxidant, and insecticidal activities of essential oils from Thymus vulgaris L., Salvia officinalis L., and Ocimum basilicum L.
Abstract The essential oils from Thymus vulgaris, Salvia officinalis, and Ocimum basilicum wereextracted by hydrodistillation, characterized by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry,and quantified by gas chromatography/flame ionization detector. The principal constituents were thymol, ρ-cymene and carvacrol (T. vulgaris); camphor, β-pinene, and 1,8-cineole(S. officinalis); and (E)-anethole, linalool, and 1,8-cineole (O. basilicum). The essential oil fromT. vulgaris was the […]
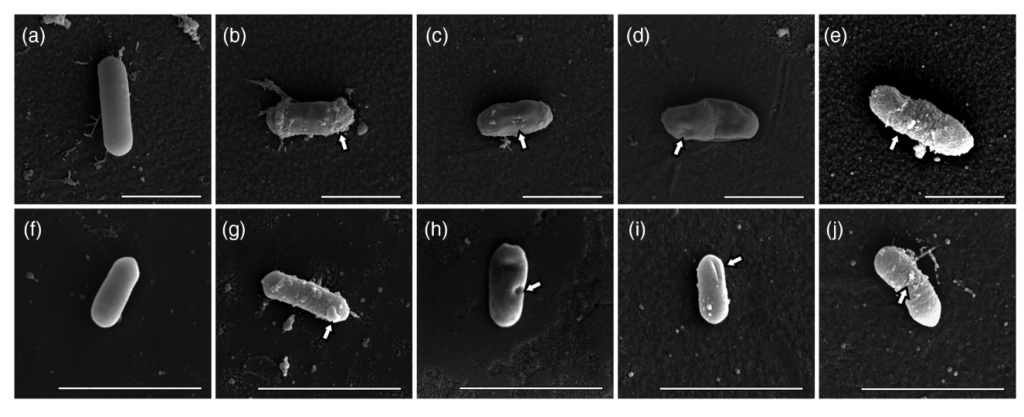
Characterization of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) rhizosphere associating rhizobacteria against Botrytis fabae AAUBF-12 and their plant growth-promoting properties
Abstract The rhizobacteria are known to protect plants from different pathogens acting as biocontrol agents and promote growth of plants. This study was conducted to isolate, screen and identify faba bean associating rhizobacteria for their antagonistic properties against Botrytis fabae AAUBF-12 and plant growth-promoting properties under in vitro conditions. In the dual culture assay, the isolates inhibited the mycelia […]
A commercial formulation of Bacillus subtilis induces metabolomic changes in root exudates that invert the chemotactic responses of the nematode Meloidogyne incognita to host and non‐host plants
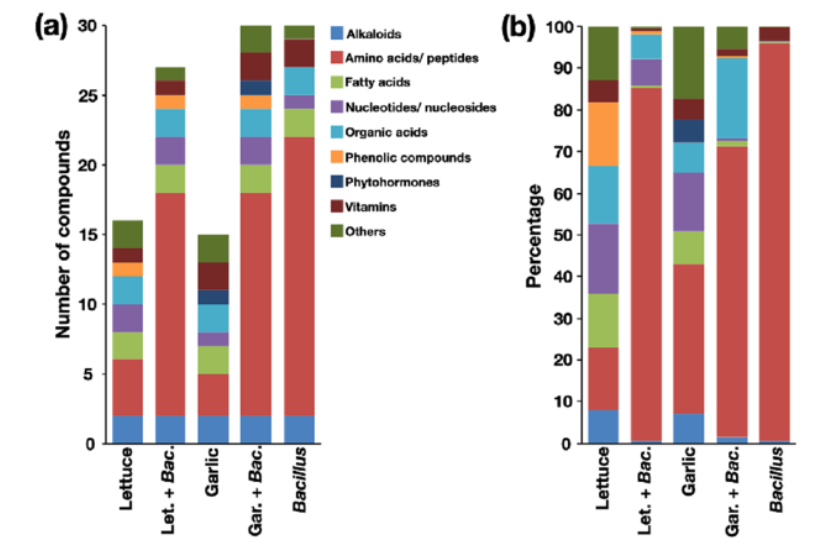
Abstract Root exudates mediate plant interactions in the environment, and they are affected by physical, chemical and biological factors. Biocontrol agents can modify root exudates and influence plant–pathogen interactions. In this study, we showed that lettuce (Lactuca sativa), a host of the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita, produced root exudates that attracted the second-stage juveniles (J2s) […]
Seed treatment with prodigiosin controls damping-of of cucumber caused by Pythium ultimum
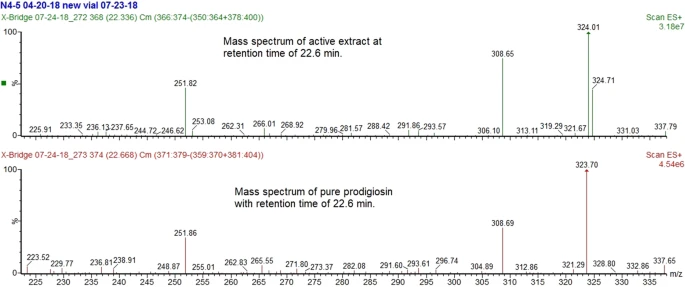
Abstract Ethanol extract of cell mass of Serratia marcescens strain N4-5, when applied as a treatment to cucumber seed, has been shown to provide control of the oomycete soil-borne plant pathogen Pythium ultimum equivalent to that provided by a seed-treatment chemical pesticide in some soils. Two dominant compounds in this extract, prodigiosin and the serratamolide serrawetin W1, were identified […]
Burkholderia perseverans sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from the Restinga ecosystem, is a producer of volatile and difusible compounds that inhibit plant pathogens
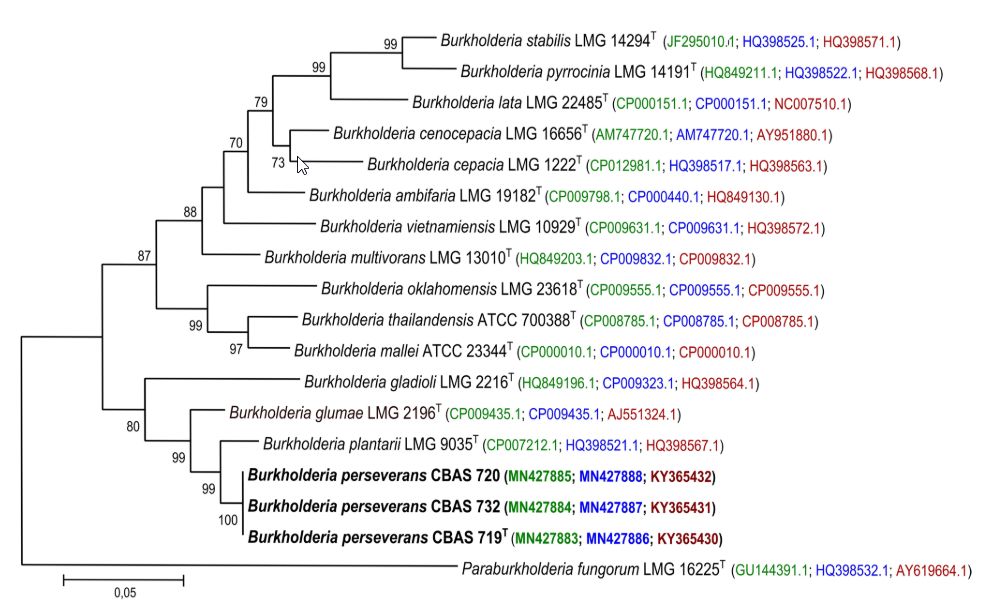
Abstract Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped, non-spore-forming, motile bacteria, designated CBAS 719 T, CBAS 732 and CBAS 720 were isolated from leaf litter samples, collected in Espírito Santo State, Brazil, in 2008. Sequences of the 16S rRNA, gyrB, lepA and recA genes showed that these strains grouped with Burkholderia plantarii LMG 9035 T, Burkholderia gladioli LMG 2216 T and Burkholderia glumae LMG 2196 T in a clade of phytopathogenic Burkholderia species. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization experiments and […]
Trichoderma: USO NA AGRICULTURA
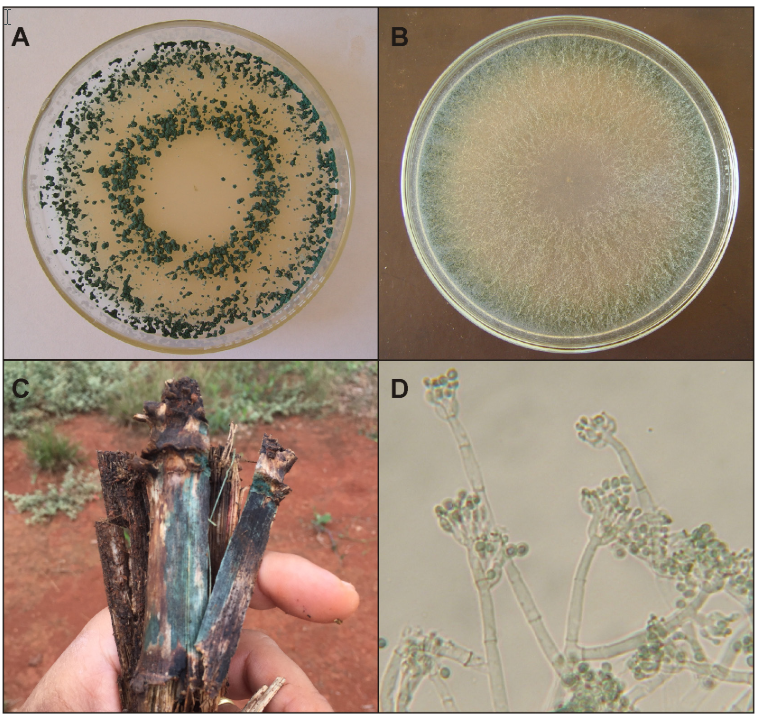

Resumo PARTE I – CENÁRIOS: Capítulo 1: Uso atual e perspectivas do Trichoderma no Brasil. Capítulo 2: Produtos comerciais à base de Trichoderma. PARTE II – TAXONOMIA E FISIOLOGIA: Capítulo 3: O gênero Trichoderma. Capítulo 4: Trichoderma e seus mecanismos de ação para o controle de doenças de plantas. Capítulo 5: Trichoderma: metabólitos secundários. Capítulo […]
The combination of two Bacillus strains suppresses Meloidogyne incognita and fungal pathogens, but does not enhance plant growth
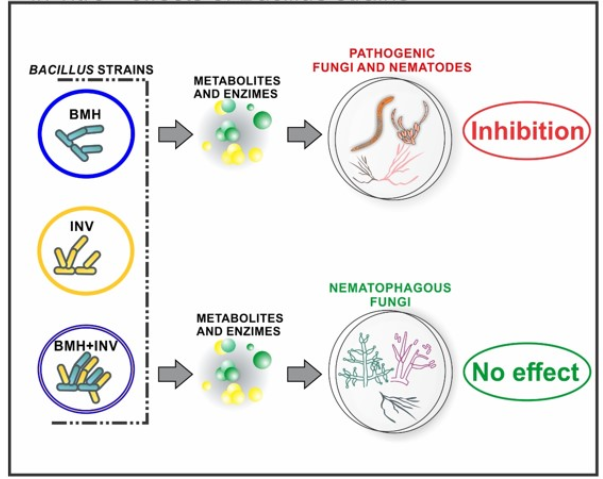
Abstract The rhizosphere is a narrow and dynamic region of plant root-soil interfaces, and it’s considered one of the most intricate and functionally active ecosystems on the Earth, which boosts plant health and alleviates the impact of biotic and abiotic stresses. Improving the key functions of the microbiome via engineering the rhizosphere microbiome is an emerging tool for improving plant growth, resilience, […]
Assessing the functional diversity of rhizobacteria from cacao by partitioning root and shoot biomasses
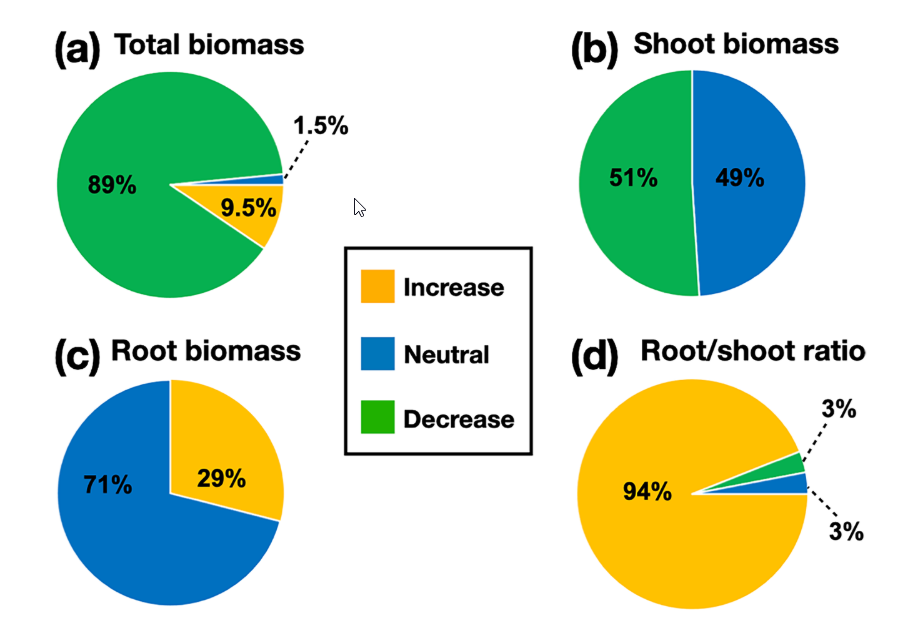
Abstract Plant-microbe interactions are critical for the sustainability of agricultural production. In this study, our aims were to characterize the genetic and functional diversity of the culturable bacterial community associated with the cacao rhizosphere and access their potential for growth promotion of cacao seedling. Culture-dependent and molecular methods were used to characterize the population densities […]

